当贝市场安卓版

- 文件大小:11.54MB
- 界面语言:简体中文
- 文件类型:Android
- 授权方式:5G系统之家
- 软件类型:装机软件
- 发布时间:2024-10-16
- 运行环境:5G系统之家
- 下载次数:278
- 软件等级:
- 安全检测: 360安全卫士 360杀毒 电脑管家
系统简介
区块链在英文中被称为 "Blockchain"。
What is Blockchain?

Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in the digital world, reshaping industries and sparking a new wave of innovation. But what exactly is blockchain, and why has it garnered so much attention?
Definition of Blockchain
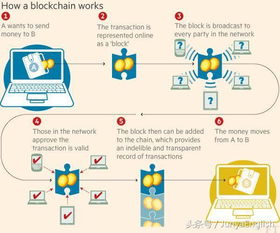
At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network.
How Blockchain Works

Blockchain operates on a network of computers, known as nodes, which are spread across the globe. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain, and when a new transaction occurs, it is broadcast to all nodes. Nodes then validate the transaction using consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), and once validated, the transaction is added to a new block.
Decentralization

One of the key features of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single entity or authority controls the data, blockchain distributes the data across a network of computers. This decentralization ensures that no single point of failure can bring down the entire system and enhances security, as altering the data requires consensus from the majority of the network.
Consensus Mechanisms

Consensus mechanisms are crucial for the operation of a blockchain. They are responsible for validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain. Different blockchains use different consensus mechanisms, such as PoW, PoS, Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and others. Each mechanism has its own advantages and trade-offs, affecting the network's scalability, security, and energy consumption.
Security and Immutability

Blockchain is known for its high level of security. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted. This is due to the cryptographic techniques used, such as hashing and digital signatures, which ensure the integrity and authenticity of the data. The decentralized nature of blockchain also makes it resistant to hacking and cyber attacks.
Applications of Blockchain

Blockchain technology has the potential to disrupt various industries, including finance, supply chain, healthcare, real estate, and more. Some of the most notable applications include:
Bitcoin and Cryptocurrencies: The first and most famous application of blockchain is Bitcoin, a decentralized digital currency.
Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They are used to automate transactions and agreements.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi leverages blockchain to create financial services that are open, accessible, and transparent.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to track and verify the movement of goods and services, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its numerous benefits, blockchain technology also faces challenges and limitations:
Scalability: As the number of transactions increases, some blockchains struggle to handle the load, leading to slower processing times and higher transaction fees.
Energy Consumption: Some consensus mechanisms, like PoW, are energy-intensive, raising concerns about their environmental impact.
Regulatory Hurdles: The evolving nature of blockchain technology often outpaces regulatory frameworks, leading to legal uncertainties.
Conclusion

Blockchain technology is a transformative force that is reshaping the way we interact with data and conduct transactions. Its decentralized, secure, and transparent nature has the potential to revolutionize various industries. As the technology continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how blockchain will impact our future.
常见问题
- 2025-03-05 梦溪画坊中文版
- 2025-03-05 windows11镜像
- 2025-03-05 暖雪手游修改器
- 2025-03-05 天天动漫免费
装机软件下载排行